Innovative Uses a Galvanometer Scanner in Industrial Automation and Control
Innovative Uses a Galvanometer Scanner in Industrial Automation and Control
Blog Article
Secret Applications of a Galvanometer Scanner in Numerous Scientific Study Fields
Galvanometer scanners have actually ended up being important to different clinical research study fields, using enhanced precision in applications varying from biomedical imaging to environmental tracking. Their ability to assist in high-resolution imaging strategies, such as confocal microscopy, plays a critical function beforehand our understanding of cellular structures. In material processing, these tools boost the accuracy of laser cutting and welding. As we check out the multifaceted applications of galvanometer scanners, it becomes evident that their impact prolongs much beyond mere technological abilities, raising inquiries about their future potential in emerging research study areas.
Biomedical Imaging
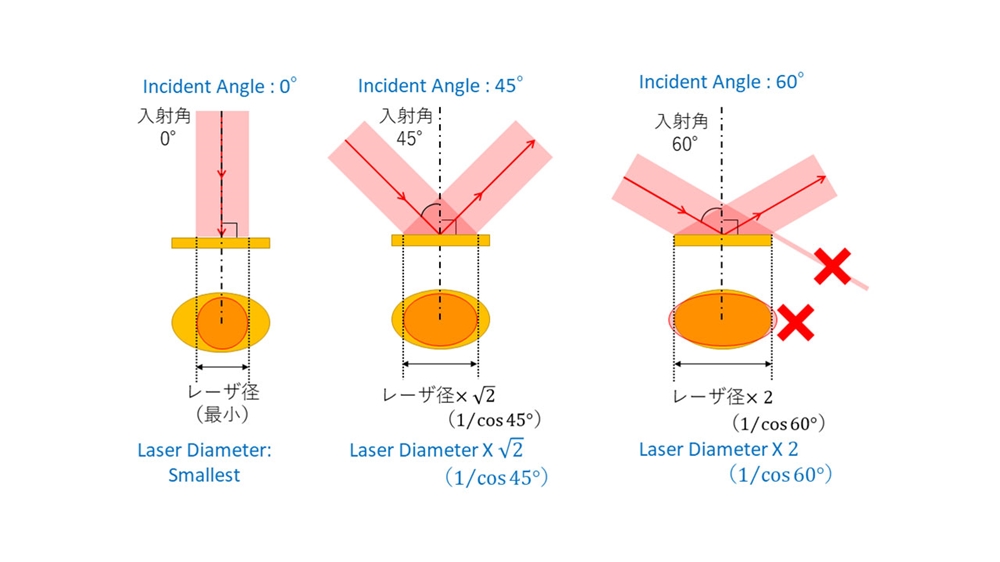
In confocal microscopy, galvanometer scanners assist in the acquisition of pictures with improved resolution and comparison, enabling researchers to visualize cellular parts in vivo. The capability to swiftly catch numerous focal planes enhances the three-dimensional reconstruction of tissues, offering essential insights right into their design and feature.

Additionally, the quick scanning capacities of galvanometer systems contribute to developments in vibrant imaging applications, such as checking cellular actions to stimuli. Therefore, galvanometer scanners are vital devices in the field of biomedical imaging, progressing study and scientific diagnostics through their precision and effectiveness.
Material Handling
Accuracy in material handling is critical for attaining high-quality cause different industrial applications (galvanometer scanner). Galvanometer scanners play an essential function in improving this accuracy by making it possible for precise and fast motion control throughout the processing of materials such as metals, polymers, and porcelains. These gadgets assist in methods like laser welding, cutting, and inscription, which need finely-tuned adjustments to guarantee ideal end results
In laser cutting, for example, galvanometer scanners enable intricate designs to be performed with high integrity, reducing waste and boosting manufacturing efficiency. The quick motion capabilities enable quick changes in the laser light beam course, which is vital for preserving consistent reducing top quality across varying product thicknesses. In a similar way, in laser welding applications, the accuracy supplied by galvanometer scanners ensures solid joints with very little thermal distortion, thus improving architectural honesty.
Additionally, the adaptability of galvanometer scanners to various laser types and wavelengths better broadens their utility in material handling. Their ability to work in tandem with innovative software application for real-time surveillance and control adds an additional layer of sophistication, making it possible for suppliers to achieve precise specs tailored to particular applications. Therefore, galvanometer scanners are important ahead of time the capacities of material processing innovations.
Optical Characterization
In the realm of optical characterization, the function of galvanometer scanners ends up being progressively substantial as they help with the analysis of numerous optical residential or commercial properties with high precision. These tools make it possible for accurate control of laser beams, enabling scientists review to methodically penetrate products at multiple angles and regularities. This ability is crucial for identifying the refractive index, absorption coefficient, and scattering properties of diverse products.
Galvanometer scanners are especially efficient in strategies such as optical comprehensibility tomography (OCT) and laser-induced fluorescence (LIF), where quick scanning is essential. By attaining high-speed modulation of the laser position, galvanometer scanners boost the temporal resolution of these approaches, resulting in improved imaging and evaluation. In addition, they enable the expedition of complicated communications between light and matter, which is important for understanding product habits under various conditions.
Furthermore, the assimilation of galvanometer scanners with spectroscopic techniques expands their utility, allowing for thorough spectral analysis across a large range of wavelengths. This convenience makes them crucial tools in areas such as products scientific research, biomedical research study, and nanotechnology, where in-depth optical characterization is extremely important for progressing expertise and innovation.

Laser Micromachining
The arrival of laser micromachining has actually reinvented producing processes, enabling the production of intricate frameworks with unequaled precision. This method utilizes high-intensity laser beams to specifically eliminate material from a substratum, making it feasible to produce micro-scale components that are critical in numerous markets. The application of galvanometer scanners in laser micromachining enhances the efficiency and accuracy of this process by enabling precise and fast beam positioning.
Galvanometer scanners help with the dynamic control of laser beams, enabling complicated patterns to be etched or cut with high integrity. Their fast reaction times and high-resolution capacities enable the manipulation of laser pulses, which is essential for accomplishing the preferred product buildings and surface area coatings. This modern technology is particularly useful in markets such as electronics, where the miniaturization of parts is important for performance improvement.
In addition, laser micromachining this content is increasingly being utilized in the medical area for making accuracy tools and implants. The mix of laser modern technology and galvanometer scanning not just streamlines production operations yet additionally lowers waste and enhances overall material usage, making it a sustainable choice for contemporary manufacturing obstacles.
Environmental Surveillance
Environmental tracking has come to be increasingly vital in evaluating and managing the wellness of ecosystems and city environments. The integration of galvanometer scanners in this area makes it possible for exact, rapid, and efficient data collection, helping with far better decision-making processes. These scanners are proficient at directing laser light beams or sensing units throughout numerous surfaces, enabling high-resolution mapping of ecological specifications such as air high quality, dirt composition, and water air pollution.
In air high quality monitoring, galvanometer scanners can be utilized to examine particle matter and gaseous pollutants, supplying real-time data that informs public health and wellness campaigns. For water quality evaluations, these scanners can aid in identifying contaminants and determining physical specifications, thus guaranteeing compliance with environmental guidelines. Furthermore, in remote picking up applications, galvanometer scanners boost the ability of satellite and drone systems to catch comprehensive pictures and information of huge areas, identifying anthropogenic influences and ecological modifications.
The versatility and precision of galvanometer scanners make them essential devices in ecological monitoring, adding considerably to lasting growth efforts and the defense of natural resources. As the need for reliable ecological management expands, the duty of these advanced devices will undoubtedly broaden additionally.
Conclusion
In recap, galvanometer scanners work as necessary tools across several scientific research study domain names. Their application in biomedical imaging enhances the accuracy of techniques vital for mobile visualization and diagnostics. In product processing, these scanners assist in innovative laser cutting and welding processes, ensuring minimal distortion. Their role in ecological monitoring emphasizes the significance of precise information collection in resolving public wellness and environmental challenges. The versatility and efficiency of galvanometer scanners remain to drive advancements in these vital fields.
In laser welding applications, the accuracy supplied by galvanometer scanners makes certain strong joints with minimal thermal distortion, thus boosting architectural stability.
In addition, the adaptability of galvanometer scanners to various laser types and wavelengths even more widens their utility in product processing. By accomplishing high-speed modulation of the laser placement, galvanometer scanners enhance the temporal resolution of these methods, leading to boosted imaging and analysis. The application of galvanometer scanners in laser pop over to this web-site micromachining improves the effectiveness and precision of this procedure by allowing exact and rapid beam of light positioning.
Galvanometer scanners help with the vibrant control of laser beams, making it possible for complicated patterns to be etched or reduced with high fidelity.
Report this page